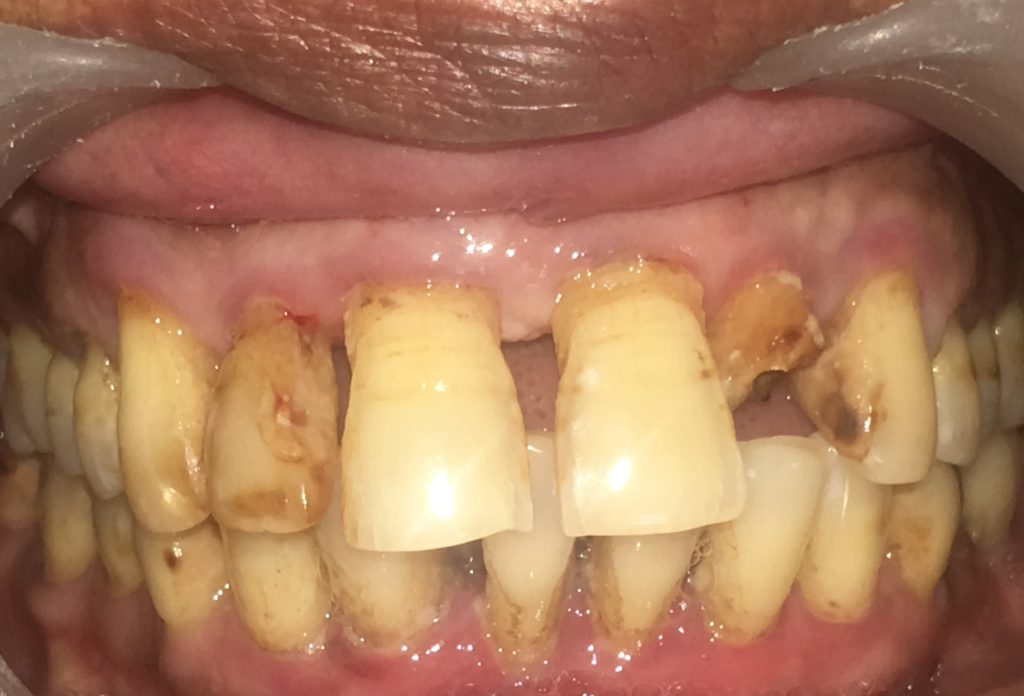
Pyorrhea, medically known as periodontitis, is a severe gum infection that damages the soft tissue and destroys the bone that supports your teeth. Left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and has also been linked to other systemic health issues like heart disease and diabetes.
Let’s explore this silent yet serious dental disease and how you can protect yourself from it.
🧪 What is Pyorrhea?
Pyorrhea is an advanced stage of gum disease that usually begins with plaque buildup due to poor oral hygiene. If not removed, plaque hardens into tartar, leading to inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) and eventually periodontitis (pyorrhea).
🔍 Common Causes of Pyorrhea
- Poor Oral Hygiene – Irregular brushing and flossing lead to plaque buildup.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use – Weakens gum tissue and immune response.
- Uncontrolled Diabetes – Reduces the body’s ability to fight infection.
- Poor Nutrition – Especially vitamin C deficiency.
- Hormonal Changes – Especially during pregnancy or menopause.
- Genetics – Family history can increase susceptibility.
- Stress – Affects immune function and healing.
⚠️ Symptoms of Pyorrhea
Early detection is key! Watch out for:
- Bleeding gums (especially while brushing)
- Swollen, red, or tender gums
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Receding gums or loose teeth
- Pus between teeth and gums
- Pain while chewing
If you’re experiencing any of these, consult a dentist immediately.
🛡️ How to Prevent Pyorrhea
Good oral care habits and a healthy lifestyle are your best defense:
✅ Brush twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush
✅ Floss daily to remove hidden plaque
✅ Use an antibacterial mouthwash
✅ Eat a balanced, vitamin-rich diet
✅ Avoid tobacco and reduce alcohol
✅ Visit your dentist every 6 months for cleaning and checkups
🏥 Treatment Options for Pyorrhea
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition:
1. Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing)
Removes tartar and bacteria from tooth surfaces and under the gums.
2. Antibiotics
Topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed to control infection.
3. Surgery
In severe cases, flap surgery, bone grafts, or tissue regeneration may be needed to repair damaged bone and gum tissue.
4. Laser Therapy
An advanced, less painful option that targets infected gum tissue with precision.
💡 Natural Remedies (Complementary)
While not substitutes for professional care, these may help:
- Saltwater rinse to reduce inflammation
- Oil pulling (coconut or sesame oil)
- Clove oil for temporary relief from pain
- Neem for its antibacterial properties
Always consult your dentist before trying any natural remedy.
🧠 Pyorrhea & Your Overall Health
Did you know? Studies link gum disease to:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Diabetes complications
- Respiratory infections
- Pregnancy complications
Taking care of your gums means taking care of your whole body.
✨ Final Thoughts
Pyorrhea is more than just a dental problem — it’s a whole-body health risk. The good news? It’s highly preventable and treatable when caught early.
🦷 Your smile is worth protecting — make oral health a priority today!
🔗 Related Links & Resources
- American Dental Association – Gum Disease
- Mayo Clinic – Periodontitis
- National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research
📢 SEO-Friendly Tags & Hashtags
Tags: Pyorrhea, Periodontitis, Gum Disease, Oral Hygiene, Dental Health, Bleeding Gums, Tooth Decay
Hashtags:
#Pyorrhea #GumDisease #OralCare #DentalHealth #HealthyGums #StopBleedingGums #SmileCare #PeriodontitisAwareness #ToothCareTips


